Oct 27, · The results chapter of a thesis or dissertation presents your research results concisely and objectively. In quantitative research, for each question or hypothesis, state: The type of analysis used; Relevant results in the form of descriptive and inferential statistics; Whether or not the hypothesis was supported Real Statistics Support. Real Statistics Function: The Real Statistics Resource Pack contains the following functions. SHAPIRO(R1, FALSE) = the Shapiro-Wilk test statistic W for the data in R1. SWTEST(R1, FALSE, h) = p-value of the Shapiro-Wilk test on the data in R1. SWCoeff(n, j, FALSE) = the jth coefficient for samples of size n Jul 08, · Getting Descriptive Statistics Using the Drop-down Menus. To run the Descriptives command using the drop-down menus, click Analyze > Descriptive Statistics > Descriptives. From the left menu, select the variable(s) you wish to run the descriptives command on, and use the arrow button to move them to the Variable(s) box
Questionnaire - Wikipedia
Our tutorials reference a dataset called "sample" in many examples. If you'd dissertation using descriptive statistics to download the sample dataset to work through the examples, dissertation using descriptive statistics, choose one of the files below:. SPSS syntax is a programming language that is unique to SPSS. It allows you to write commands that run SPSS procedures, rather than using the graphical user interface.
Syntax allows users to perform tasks that would be too tedious or difficult to do using the drop-down menus. This is the case when you are re-running the same analysis many times, or doing complex transformations on data.
Syntax also provides a record of how you transformed and analyzed your data, and allows you to instantly reproduce those steps at any time. Note that the two methods of interacting with SPSS—drop-down menus and syntax—are not mutually exclusive. You can use both methods if you wish they will produce the same resultsor switch from one method to the other depending on the actions you want to perform and your comfort level with menus or syntax. A comment is a line of text in a program that is not read by the computer as a command.
Comments do not affect how the program functions; they exist purely for the humans reading and writing the program. Comments help the reader understand what the program is doing. In general, it is good practice to use brief but descriptive comments in your code. Your comments should be clear enough that a reader completely unfamiliar with your work can understand what your program is doing. Hitting the Enter key will create a new, dissertation using descriptive statistics, un-commented line.
Typically, comments in SPSS syntax are color-coded with the color gray. After you've opened a Syntax Editor window, you can start writing your syntax directly in this window. After clicking the Paste button, dissertation using descriptive statistics new syntax will automatically be added to your open Syntax Editor window. sps file so that you can re-use it later. You can do this from any open window including the Data View or Output View. This is convenient if you wish to review what commands you ran or if you want to edit or save the syntax commands for future use.
Click File Locations and you will see the pathname for the Journal File in the Session Journal area. You can also change the location where this file is stored. Find the folder in which the Journal File is stored. Select this file and click Open. Dissertation using descriptive statistics you can see the commands you ran during the most recent SPSS session.
You can also save this file for future use. Here is an example of how to run the same command using both drop-down menus and syntax. Although we could choose any command, we will run a simple descriptives command on the variable height in our sample data set. From the left menu, select the variable s you wish to run the descriptives command on, and use the arrow button to move them to the Variable s box.
In this example, we select the variable Height. Click OK. Notice that there is also syntax printed above the descriptive statistics in the output. The syntax provides a text-based map of the command we just ran using drop-down menus. If we had executed this syntax in a Syntax Editor window instead, we would get the exact same results as we did using the drop-down menu. Reopen the Descriptives procedure, dissertation using descriptive statistics.
All of your previous settings should still be active. Instead of clicking OK, click Paste. This should open a new Syntax Editor file with the descriptives syntax in it. Notice that that the text in the dissertation using descriptive statistics editor appears in certain colors, and some words become bold. These stylistic formats simply define different parts of the syntax command. When you are finished typing the syntax, you need to tell SPSS to run the command by clicking the green arrow at the top of the window.
We have produced the very same output using both drop-down menus and syntax. Note: You can copy the syntax from an output window and paste it into a new Syntax Editor window to re-use, modify, and save the syntax. To copy syntax from the output in the Output Viewer windowsimply click the syntax, copy it, and paste it into a Syntax Editor window. For example, perhaps I decide that I want to look at some different variables, English and Writing, and I would like to get the dissertation using descriptive statistics statistic instead of the minimum and maximum.
I can easily modify the syntax I already have to accommodate these changes:. Now when SPSS runs the descriptives command, dissertation using descriptive statistics, it shows the range, mean, and standard deviation for the variables English and Writing. After the previous example, dissertation using descriptive statistics, it may seem like the menus are easier to use than syntax. So why would anyone want to use syntax? The biggest benefits of using SPSS syntax are reproducibility and communication.
It is far easier to "retrace your steps" with syntax if you need to recall the modifications you've made to your dataset. It's also far easier to find and correct mistakes in your analysis if you have the syntax, as opposed to if you had used the menus. Syntax can easily be modified and re-used on future projects, saving you time and effort in the long run.
If you are a Qualtrics user and have downloaded your "raw" survey data in SPSS format, using syntax to modify variable labels or compute new variables means that you don't have to worry if you lose the SPSS data file you've been working in; you can just re-download the raw data from Qualtrics and rerun your syntax to get your data back. It is much easier to communicate to others what actions you performed in SPSS by showing dissertation using descriptive statistics your syntax than it is to describe how you used the menus.
The content of the menus and dialog windows has changed over time with each version of SPSS, while the syntax has remained relatively unchanged though there are a few notable exceptions. In general, if you are working on a major project like a thesis, dissertation, or research for publicationor if you are collaborating with others on data analysis, we strongly recommend using SPSS syntax. The example above is only the beginning of learning how to write syntax commands.
You can begin learning syntax by using the dropdown menus to call certain procedures and then clicking the Paste button to have SPSS write the corresponding syntax to a syntax file.
You can also check out the Command Syntax Reference guide, which outlines all of the rules for writing syntax and provides examples. This will open a PDF dissertation using descriptive statistics the reference manual. Kent State University LibGuides Statistical Consulting SPSS Tutorials Using SPSS Syntax. Search this Guide Search. SPSS Tutorials: Using SPSS Syntax SPSS syntax is a programming language unique to SPSS that allows you to perform analysis and data manipulation in ways that would be tedious, difficult, or impossible to do through the drop-down menus.
This tutorial introduces the basics of using syntax. Home Getting Started with SPSS The SPSS Environment The Data View Window Using SPSS Syntax Data Creation in SPSS Dissertation using descriptive statistics Data into SPSS Variable Types Date-Time Variables in SPSS Defining Variables Creating a Codebook Working with Data Toggle Dropdown Computing Variables Recoding Variables Recoding String Variables Automatic Recode Weighting Cases rank transform converts a set of data values by ordering them from smallest to largest, and then assigning a rank to each value.
In SPSS, the Rank Cases procedure can be used to compute the rank transform of a variable. sps Syntax to add variable labels, value labels, set variable types, and compute several recoded variables used in later tutorials.
What is Syntax? Basic Syntax Rules Formatting Statements in SPSS end with a period. SPSS syntax is not case-sensitive. You can use all lower case, all upper case, or a mixture of both when writing syntax.
Comments A comment is a line of text in a program that is not read by the computer as a command. Color-Coding By default, SPSS uses color and bolding to indicate the roles of the words in the syntax. Example: Comparing Drop-Down Menus versus Syntax Here is an example of how to run the same command using both drop-down menus and syntax. The results for the command will appear in the Output Viewer window.
When should I use syntax? Reproducibility It is far easier to "retrace your steps" with syntax if you need to recall the modifications you've made to your dissertation using descriptive statistics. Communication It is much easier to communicate to others what actions you performed in SPSS by showing someone your syntax than it is to describe how you used the menus, dissertation using descriptive statistics.
Learning Syntax The example above is only the beginning of learning how to write syntax commands. Report a problem. Subjects: Statistical Software. Tags: statisticstutorials. University Libraries. Street Address Risman Dr. Kent, Ohio Mailing Address PO Box Kent, OH Contact Us library kent. Facebook Facebook. Twitter Twitter. Flickr Flickr. Instagram Instagram. Youtube Youtube. Quick Links How Are We Doing?
Give to University Libraries Student Jobs Ask Us.
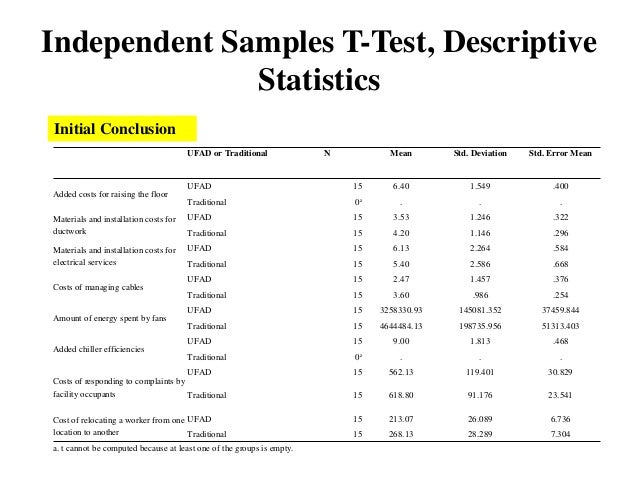
Quantitative Research - Descriptive Statistics
, time: 11:06How to Write the Dissertation Discussion Chapter | Research Prospect

Jul 08, · Getting Descriptive Statistics Using the Drop-down Menus. To run the Descriptives command using the drop-down menus, click Analyze > Descriptive Statistics > Descriptives. From the left menu, select the variable(s) you wish to run the descriptives command on, and use the arrow button to move them to the Variable(s) box Nov 07, · How to Write the Abstract for the Dissertation. Using Subsections and Subheadings. You might want to reflect the structure of the discussion in your organization of the dissertation discussion chapter, and for that, you will need to create sub-sections. It is important to keep subsections to the point and as short as possible Real Statistics Support. Real Statistics Function: The Real Statistics Resource Pack contains the following functions. SHAPIRO(R1, FALSE) = the Shapiro-Wilk test statistic W for the data in R1. SWTEST(R1, FALSE, h) = p-value of the Shapiro-Wilk test on the data in R1. SWCoeff(n, j, FALSE) = the jth coefficient for samples of size n

No comments:
Post a Comment